Gyeeta Architecture
Gyeeta is a free, Open Source Observability tool utilizing eBPF and Linux kernel statistics.
Components in Gyeeta
Gyeeta consists of the following components :
Host Monitor Agent (named
partha) to be installed on each of the hosts which needs to be monitoredA Central Server (named
shyama) which serves as both an Aggregating Server and an Alert ManagerOne or more Intermediate Servers (named
madhava) analyzing metrics from multiple monitored hosts (partha)A NodeJS Webserver which handles Web UI and REST API queries
An Alert Agent which interacts with
shyamaAlertManager and executes the Alert Trigger Actions (Notifications)One or more Postgres DBs to be used as the datastore for
shyamaandmadhavaservers
The image below shows the high level overview of how the different components interact with each other :
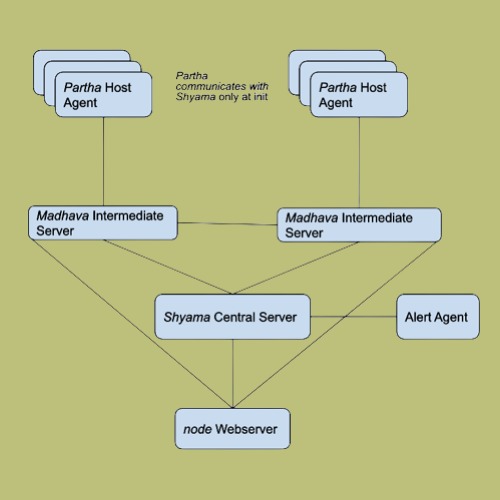
Highly Scalable
Gyeeta supports monitoring of tens of thousands of hosts using a single shyama instance and multiple madhava instances.
Partha Host Monitor Agent
The Gyeeta Host Monitor Agent (named partha) needs to be installed on every host that is to be monitored and preferably started at init (startup) so that all process
activity can be monitored.
The partha application is a lightweight priviliged process using eBPF and Kernel Statistics to monitor all activities on each monitored host.
It can monitor hosts with thousands of connections, hundreds of processes/sec, or tens of thousands of queries/sec, all with under 10% single core CPU utilzation.
Features :
- Monitors all Services and gathers statistics such as Queries/sec, Response Time (Latency), HTTP Errors (for HTTP services)
- Monitors all Network Flows within host and across hosts as well and correlates them with
madhava - Monitors Host and Processes Resource usage
- Auto detects any anomalies and flags any Degradation in Host, Service or Process performance including CPU, Memory or IO Contention
- Monitors all services with statistics for all TCP traffic. Does not use sampling.
- Interacts with a single
shyamaassignedmadhavaIntermediate Server and sends all statistics over a TCP connection - No local disk storage is needed as all data is sent to the Intermediate server
- Lightweight with max 10% of one CPU core (p99 4% of one core) (averaged over a 5 sec interval) and max 300 MB RSS Memory
Learn more from links below :
Partha Agent Installation and Host Requirements
Shyama Central Server
The shyama Central Server serves as both an Aggregating Server and an Alert Manager and is the only component which interacts with all
other components.
A single shyama instance needs to be installed on any Linux host with minimal CPU and RAM requirements. The shyama
instance needs to have Network Connectivity with all monitored hosts and all madhava instances.
Features :
- Assigns appropriate
madhavaintermediate servers to each of the monitored hosts (partha) based on Network adjacency and availability. - Acts as the Alert Manager and co-ordinates Alert Trigger Actions with the Alert Agent
- Coordinates with the one or more
madhavato resolve Network Flow Dependencies - Tracks Cluster wide Service and other Statistics
- Uses Postgres DB as the datastore to store Cluster and Global level statistics including Alerts
- Communicates with the Monitored Hosts
parthainstances only at theparthastartup while assigningmadhavainstances to eachpartha. This limits inter-region network communication if theshyamainstance is in a separate region fromparthahost - Communicates with the Webserver for web query responses
- Optional Redundancy in Active Passive modes with one active and one or more passive
shyamainstances
Learn more from links below :
Madhava Intermediate Server
The madhava Intermediate Server analyzes the monitored Host Statistics and interacts with partha Host Agents, shyama Central Server, other
madhava server instances and the Webserver.
The number of madhava instances to be installed depends on the number of monitored hosts and Network Connectivity (adjacency) requirements.
Features :
- Single
madhavainstance can handle upto 500 Hosts (partha) interaction and monitoring depending on themadhavahost CPU and RAM specs - Coordinates with
shyamaand othermadhavainstances to resolve Network Flow Dependencies - Uses Postgres DB as the datastore to store the data pertaining to the monitored hosts
- Communicates with the Webserver for query responses
- Optional Redundancy in Active Passive modes with one active and one or more passive
madhavainstances
It is recommended that at least one madhava server be installed in each active Network zone to limit inter-zone or
inter-region Network egress costs.
Learn more from links below :
Postgres Database
PostgreSQL is used as the datastore for shyama and madhava servers. Upto 3 madhava servers can share the same Postgres
instance as the datastore. As the number of madhava instances increase the requirement for additional Postgres instances will arise.
It is recommended to use a Postgres DB in the same Network Region/Zone as the madhava or shyama instance for better performance and lower costs.
Learn more from link below :
Node Webserver
The nodejs based webserver handles Web UI and REST queries and forwards them to the shyama and madhava servers.
A single instance of Webserver needs to be installed on a host with Network Connectivity to shyama and all madhava instances.
Features :
- Accumulates query responses from multiple
madhavaservers for Global or Cluster Level queries - Supports a minimal but powerful WebUI on default HTTP with optional HTTPS support
- A comprehensive REST API based framework is exposed both for API Querying and CRUD operations such as creating Alerts
- Currently the WebUI and REST API queries are authenticated using a fixed User Password Basic Authentication. SSO (Single Sign-on) based Authentication and Authorization using OIDC / OAuth2 is planned for a later release
- Maintains persistent connections with the
shyamaand all themadhavaservers - Multiple Webserver instances can be started for redundancy purposes
Learn more from links below :
Alert Action Agent
The Alert Action Agent is involved in executing the Alert Actions (Notifications) as per the configured Alert rules.
A single instance of the Alert agent needs to be installed on a host with Network Connectivity to shyama. If the Alert Action needs
Network connectivity to an external service such as Slack or Pagerduty, the Alert Action Host must have Internet Connectivity as well.
Features :
- Currently Gyeeta supports Email, Slack, PagerDuty, Webhooks as the Alert Action (Notification)
- Maintains persistent connections with the
shyamaserver (shyamaalso acts as the Alert Manager) - Multiple Alert Action Agents can be started for redundancy purposes
Learn more from links below :