Network Flows / Service Maps
Service Maps refer to the realtime Visual representation of the Network Traffic to and from the Services monitored.
Querying Network Flows
Gyeeta separates the Network Flows inbound to a Service from the Network Flows outbound from a Client Application.
The Inbound Network Flows to any Service is available from either the activeconn or extactiveconn subsystems. The Outbound Network Flows from any Client Application is available from either the clientconn or extclientconn subsystems.
This implies that to get the complete set of all inbound connections to a service and outbound connections from that service requires multiple API calls.
activeconn or extactiveconn always require a Service as input and act on Services alone whereas clientconn or extclientconn APIs always require a Grouped Process as input as they act on a Client Application.
Web UI Network Flows Process
The Web UI Network Flow pages execute multiple calls to show the complete Service Map.
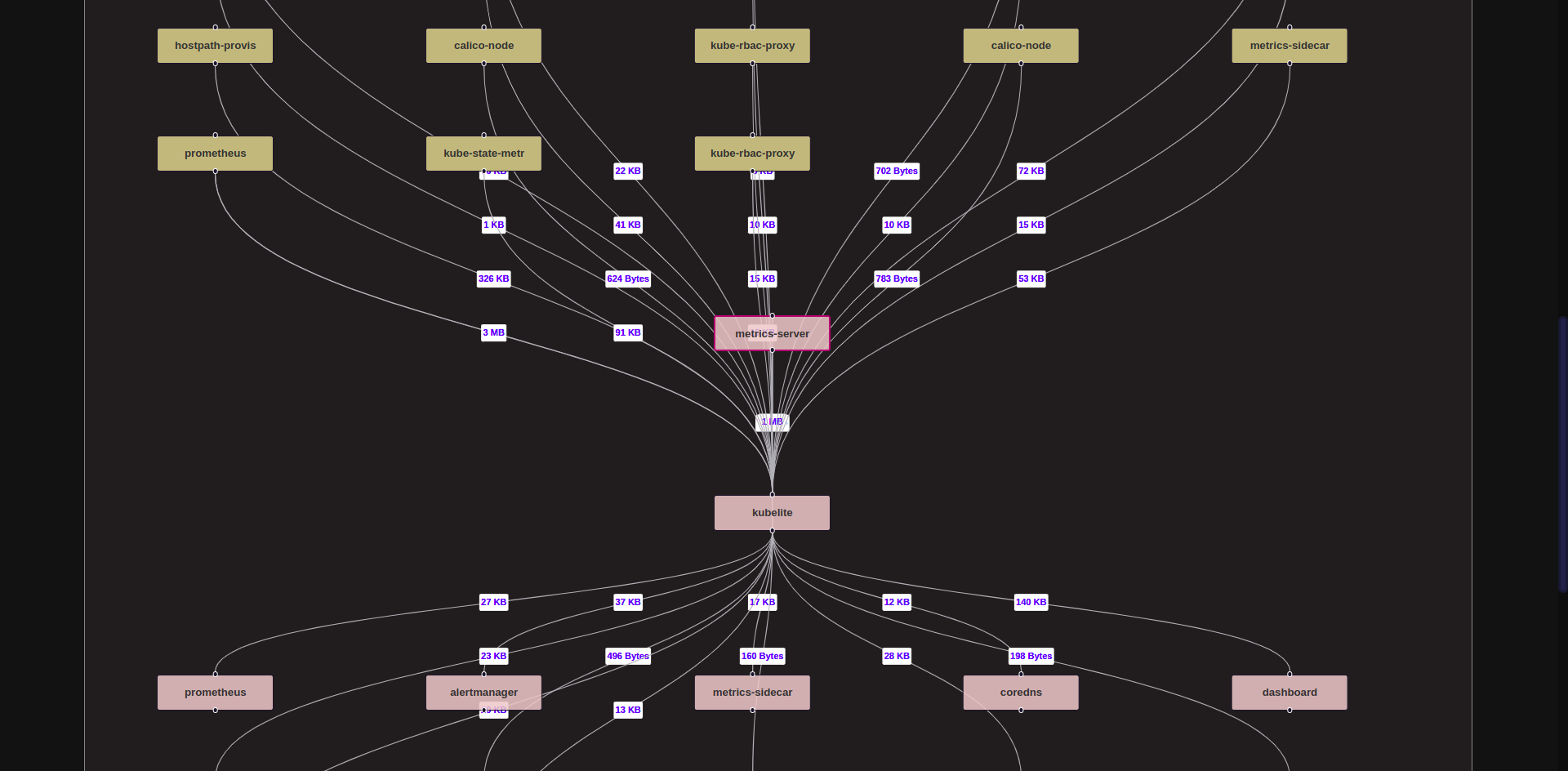
For example, for the snapshot shown above, the Web UI will execute the following steps :
- First activeconn API is called for the Service requested. This will fetch all inbound connections for the time requested.
- Next svcprocmap API is called for the Service requested. This will fetch all Grouped Processes for the Service requested.
- Thereafter, for all the Grouped Processes of that Service, clientconn APIs are called to get the complete set of outbound connections.
Network Flow Analysis across hosts
Gyeeta will correlate all Network Flows even spanning multiple hosts almost instantaneously. For connections spanning multiple hosts, Gyeeta will take up 45 sec to correlate the entire Network Flow. All Network connections are analyzed, including short lived connections.
If one of the endpoints of a Network Connection originates from a host which is not monitored using Partha Host Agent, Gyeeta will
report the endpoint as Unknown.